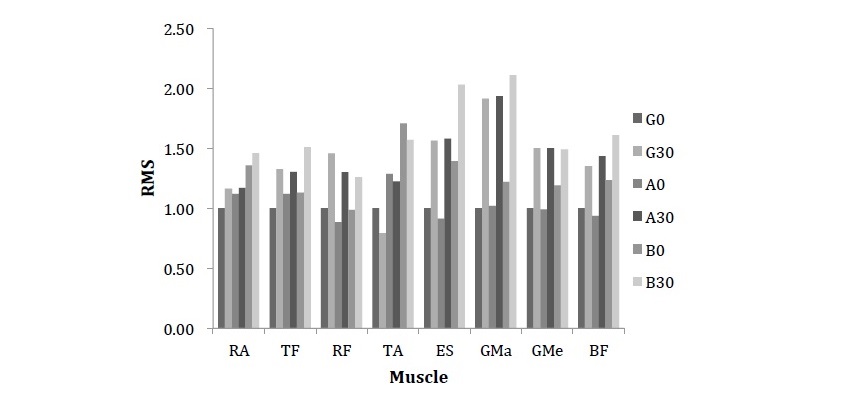
Figure1. The Value of RMS under different combination with Ground & Unstable Surfaces and Body & 30%1RM weight
Chunmei Cao
Division of Sport Science and Physical Education, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
Skill learning is often influenced by the age, cognitive abilities and motor experience of the learner. Extrinsic feedback facilitates skill acquisition if it is provided with the right timing, precision, schedule, frequency and/or error range. Older adults often experience deficits in attention, memory, executive function, processing and motor speed. Examining how functional declines mediate the extrinsic feedback effects on skill learning offers a valuable opportunity to address key issues in learning mechanisms of older adults. The purpose of this study was to understand how functional deficits of cognitive motor aging and extrinsic feedback delays influence skill learning.
There were 61 old adults (age: 68.9 ± 4.5) attending the test, who were randomly divided into experimental group (receiving extrinsic feedback) and control group (no extrinsic feedback). All the old adults were grouped into cognitively normal (CN) or cognitively impaired (CI) by the TMT-A and -B cut-off times of 60 s and 85 s. All the participants learned to perform handle task in fixed time (1000ms). After training 36 times we tested the achievement by repeat the measurement. Retest performance was indexed in two ways: absolute error (AE; ms) and variable error (VE; ms). And t-tests determined the differences between the CN and CI older learners for the times required to complete TMT-A and -B, AE and VE in the retests of both experiments.
The cognitively normal (CN) participants were significantly faster than the cognitively impaired (CI) participants in completing TMT-A and TMT-B (t (61) = 3.28, P = 0.0001, η2= 0.45).The CN had less AE and VE than the CI in the retests (t (14) = 5.77, P = 0.012, η2 = 0.39 (AE); t (14) = 5.79, P = 0.014, η2 = 0.33 (VE)).
The results suggest that the reduced cognitive functions of older adults reflected in TMT-A and TMT-B measures (e.g. visual attention, concentration, divided attention, mental flexibility, sequencing ability and executive functions) could result in an elevated level of timing errors in motor learning. The cognitive functions of older adults affected their abilities to use extrinsic feedback in learning the timing tasks.
Huihua Lan
School of Graduate, Tianjin University of Sport, Tianjin, China
Postural adjustments involve the coordination of anticipatory and compensatory postural adjustments (APAs and CPAs, respectively) to maintain and restore upright balance in response to external perturbations. However, APAs and CPAs are known to be deteriorated with increasing age. The purpose of this study was to explore the effects of aging on the ability of older adults to utilize APAs and CPAs in response to support surface translation in the sagittal plane.
Seven healthy young subjects and seven healthy older subjects participated in this study. They were asked to make a step under two experimental conditions: (1) quiet stance stepping task (QS): no translation of the support surface, subjects waited 2 seconds and then made a comfortable step after heard a word given by the experimenter, (2) forward perturbation stepping task (FS): the experimenter gave a word cue to indicate the subject that the support surface would move forward, subject made a step as soon as he/she felt the support surface's moving. Electromyography (EMG) was recorded from four lower limb muscles on the right side of the body. Electrodes were attached to the muscle belly of tibialis anterior (TA), soleus (SOL), rectus femoris (RF) and biceps femoris (BF). Ground reaction forces and moments of forces were recorded by a Kistler force platform. The forces, moments of forces and EMG signals were sampled at 1500 Hz.
The older subjects were capable of making a forward step based on the coordination of APAs and CPAs associated with the support surface translations. However, APAs were delayed and reduced in magnitude in elderly which resulted in larger CPAs and greater peak COPAP displacements following perturbations.
The results suggest that aging is associated with diminished control in the COPAP displacement in both the APAs and CPAs in response to support surface translations in maintaining upright balance.
Nan Xu
Beijing Sport University, China
To investigate the influence of loaded warm-up intervention on running economy, vertical stiffness, agile, sprint and vertical power and to determine the relationship between running economy and its potential neuromuscular characteristics.
16 healthy male athletes divided randomly into trial and control groups. Trial group warm-up with weighted vest-set in 20% body mass, while control group perform the same warm-up protocol without any load. Warm-up protocol contents 3 minutes self-paced jog and 10 dynamic stretch movements. Each participants ought to take each test before warm-up, at 6 minutes and 12minutes recovery point after warm-up. 6-min submaximal run, 2.0Hz submaximal jump, squat jump and countermovement jump, 30m sprint and 5-0-5 test are employed to determine running economy, vertical stiffness, reactive strength ratio (RSI), sprint speed and agile ability respectively. These trials are preceded in separated days with an interval over 48 hours to prevent interaction.
(1) Compared with data before warm-up: a significant increase of running economy happened in trial group at 12 minutes after warm-up (P<0.05). Speed of 30m sprint also rose significantly at 6 minutes after warm-up (P<0.05). 5-0-5 test and vertical stiffness indicated an upgrade tendency, whereas RSI indicated a decrease trend, but these variations were not significant compared with initial data before warm-up. For control group, there was no significant variation in running economy, 30m sprint, 5-0-5 test, vertical stiffness and RSI at each recovery point. (2) Loaded warm-up contributed to a significant increase in running economy at 12 minutes after warm-up compared to control group (P<0.05). Vertical stiffness increased more consistently and more rapidly after warm-up for trial group, while control group rose slightly at 6 minutes then decrease at 12 minutes after warm-up, but no significant difference between two groups at each time point (P>0.05). A tendency suggested that 30m sprint speed and 5-0-5 test increased more sharply and RSI decreased less for trail group, but no significant difference between two groups (P>0.05).
Warm-up with 20% body mass weighted-vest could contribute a significant increase in running economy. This influence may related to the improvement in vertical stiffness, sprint speed and the prevention of decrease in RSI.
Wen Dai
Shanghai university of Sport, China
Professional experience at high level leads to cortical reorganization across various brain areas. Motor cortical output increases after long-term training. However, it is not clear how cortical excitation and inhibition change with cortical plasticity after long-term training. Hence, We hypnotize that motor cortical output increases after long-term training and this is accompanied by increased motor cortical inhibition.
We tested motor-evoked potential input-output curve and short-interval intracortical inhibition in 10 elite table tennis players and 10 novices using transcranial magnetic stimulation. At first, we defined "1 mV" intensity as the minimum stimulator output that generated motor-evoked potential of more than 1 mV when the target muscle was completely relaxed and "active motor threshold" intensity as the minimum stimulator output that generated motor-evoked potential of more than 100 μV when the target muscle was performing 10% of the maximal contraction in at least 5 out of 10 trials respectively. Motor-evoked potential input-output curve was tested at transcranial magnetic stimulation intensity of 50%, 70%, 80%, 90%, 100%, 110%, 120%, 130% and 150% of "1mV". Short-interval intracortical inhibition at interstimulus interval of 2 ms was tested with a paired-pulse paradigm. Test stimulus intensity was set at "1mV". Conditioning stimulus was set at 70%, 80% and 90% AMT.
Both MEP amplitude and short-interval intracortical inhibition were increased in the athletes compared to the novices. MEP input-output curve was different between two groups with steeper slope of the curve in athletes. Short-interval intracortical inhibition increased with high Conditioning stimulus intensity. Importantly, short-interval intracortical inhibition was stronger in athletes than that in novices. The correlation between peak cortical inhibition and the slope of MEP input-output curve was significant in athletes but not in novices.
Choric and systematic physical exercises will facilitate the excitatory and inhibiting effect of cerebral corticospinal tract, and improve the recruitment level within cortex. Besides, these changes will go further with the progress in external stimulus. Both the facilitation and inhibition of cerebral cortex mean the change in the recruitment level of motor cortex cells. The synapse recombination and the generation of new synapses in primary motor cortex boost postsynaptic potentials, further facilitating the learning and control of motor skills. It should be taken into consideration in the development of new training methods for high-level athletes and new rehabilitation techniques for patients with neurological disorders.
Yang Hong
Sport Service Inspection Center, China Institute of Sport Science, Beijing, China
To determine the trunk and lower-limb muscles activity in relation to the type of load (body weight, 30%1RM) and the type of support surface (six degrees of freedom (hard), Core stability disk (soft)) for ordinary people in deep squats.
Nineteen healthy male subjects (20.1±1.1 years, height: 1.70±4.1m, mass: 62.8±6.9 kg) volunteered for the experiment 1 repetition maximum (1RM) tests (75.47±6.9 kg) were performed for squats on stable surfaces by all subjects first. A minimum of 48 hours post 1RM, subjects returned to perform 5 consecutive squats with 2 weight loads (body weight (0) and 30% 1RM (30)) on 2 unstable surfaces and ground (G). The hard unstable surface (state A) is performed on a platform with six degrees of freedom which could be programmed to rotate around any axis of rotation. For state A the six axes of rotation were found to be at x=10cm y=2cm z=2cm ax=2cm ay=2cm az=2cm, and the frequency were defined as x=0.8Hz y=0.2Hz z=0.2Hz ax=0.2Hz ay=0.2Hz az=0.2Hz. State B is on Core stability disk. In 3-dimensional environments, 8 muscles were measured by surface electromyography (sEMG) (rectus abdominis (RA), lower erector spinae (LES), rectus femoris (RF), biceps femoris (BF), tensor fascia (TF), tibialis anterior (TA), gluteus maximus (GMa), gluteus medius (GMe)) during the performance of deep squats. The sequence of 6 conditions was randomized and each subject had 2 minutes rest between conditions to avoid fatigue. A polar heart rate monitor was used to ensure subjects' heart rate were under 100b·min-1 during the process. The relative values of the average root mean square (RMS) were analyzed with ANOVA test in each subject on the basis of the condition in body weight load and ground.
The results (Figure1.) show that no difference (p>0.05) was in the RMS value of all selected muscles with bodyweight or 30%1RM weight during stable and unstable platform (hard bearing surface). On the core stability disk, which is the soft support surfaces with air filling, the RMS value of some muscles (RA, TA, ES) were significantly changed (p<0.05). Most muscles (expect TA) activation was greater as the external load increased in stable and the same instable state.
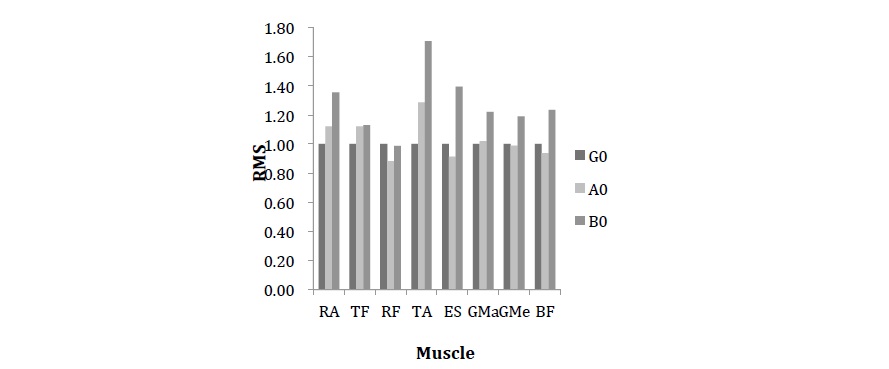
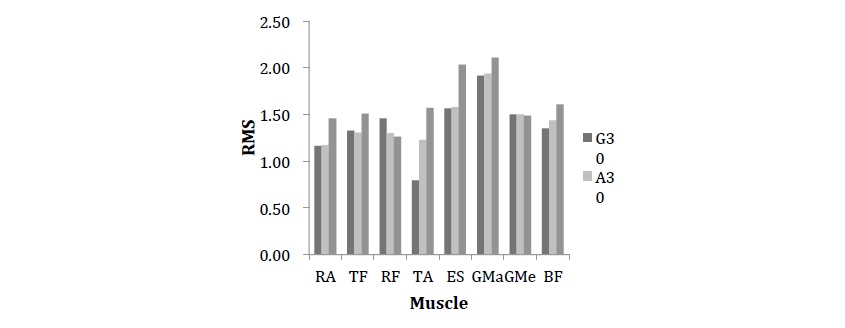

Figure1. The Value of RMS under different combination with Ground & Unstable Surfaces
and Body & 30%1RM weight
In conclusion, muscle activation is invariable for unstable training on hard bearing. The material of unstable device is another import thing with unstable degree. Load is the main factor during unstable training.
Zijian Zhao
Zhengzhou University, China
Conventional idea think strength training may hinder children's physical growth, this is a misunderstanding. People also always have underappreciated assessments of strength training, many countries put it on the fourth or the top floor of Sports Pyramid. This paper expounds the importance of strength training and proposes the key points of children's strength training to guide the children have a correct strength training.
Using the documentation method, case analysis method, comparative study method and other methods, research proves the value of strength training and proposes the key points of children's strength training.
1. It is not harmful for children to take part in scientific strength training. What's more, Research data shows that strength training is good for their growth. Although there is a risk of injury, there is no scientific evidence that early strength training will hinder children's growth and development.
2. Through strength training, children can prompt the thickening of compact bone substance, increase the sturdiness of bones, enhance the function of cardiovascular system and improve the obesity habitus. Meanwhile, strength training can also improve muscle strength obviously.
3. Children's strength training should follow individualization principle, gradually increasing load principle, special principle, reasonable interval training principle, comprehensive principle, and the principle of giving priority to the development of the muscles.
4. During childhood, the bone substance with more softness, large elasticity and mutability. Therefore, children's strength training should pay greater attention to correct postures, and not impose too much load. Besides, children's muscle fibers mainly aim to grow long. Only when the body stops growing tall, muscle fibers turn into thick with the enlargement of muscle cross-sectional area. Consequently, children's strength training should be terse and forceful, and better with long interval time.
5. Children with congenital heart disease, acute pulmonary arterial hypertension or severe pulmonary hypertension should avoid participating in strength training, because compensatory dysfunctions potentially caused by the abrupt change of hemodynamics in training can make them in danger.
Strength is the prerequisite and guarantee to move and play, there is no substitute for being strong. Strength training has a positive impact on musculoskeletal system health, mental health, prevention of cardiovascular disease and adiposity. In addition, it can not only improve the sports performance, but reduce the sports-related injuries. Therefore, we should pay attention to children's strength training.
Dongfeng Nie
Physical Education Department, Northwestern Polytechnical University, China
Based on the physical health test of 433 college students, the paper investigates their quality of life level to explore the relationship between college students' physical health status and the quality of life of physiology and psychology. The aim is to provide theoretical basis for improving the physical health and the quality of life of college students.
Some physical teachers were assigned to test the quality of life of the students according to SF-36questionmail and measure physical health indicators of the students according to the instructions laid down in "Student's physical health standard". And statistically analyze these test data with SPSS.
1) The analysis of the situation of the quality of life of college students and the dynamics of general health status: from the eight dimensions of college students' quality of life, the physiological function and social function are high, the emotional function is low, the other dimensions is in the middle level.
2) The analysis of indicators of quality of life of college students of different physical health level: from the level of life quality of different BMI of the students, there is no significant difference between male and female students. There is no significant difference in the psychological and physiological indexes of male students from the perspective of the influence of endurance level on students' quality of life, and female students have significant differences in physical function, physical pain and general health (P < 0.05).
3)The analysis of mental, physical health and physical health status of different life quality level of college students: according to the physiological and psychological indicators of college students from different quality of life, no matter males or females, the quality of life of the high level group is significantly higher than that of the low level group (P < 0.01). The physiological and psychological indicators that affect the quality of life of college students are all aspects, however, the impact of various indicators on the quality of life of college students is not the same.
1) The quality of life of college students with different physical health is not significantly different. The indicators of the internal structure of college students' quality of life tend to keep abreast with physiological indicators and the health level of the physical fitness. And psychological indicators of male and female students are different.
2) The physical health of college students with different quality life is significantly different. It remands that universities should make more researches on the mechanism of the impact of physical health on college students' quality of life, and pay more attention on dredge for the cognition and consciousness of college students' health, and to cultivate their positive physical exercise behavior.
Shuhei HIROTA
Hokusho University, Japan
Hokkaido is cold and snowy region. For that reason, outdoor activities of winter is limited. Therefore, the physical fitness and the exercise capability of children in Hokkaido is the lowest standard in an every prefecture in Japan. This is a very serious problem for Hokkaido. I work the following things in order to solve this problem. It is development of the physical fitness and the exercise capability improvement program that secure quality at the same level in school of any place without being influenced by a school scale or the characteristic and can exercise easily. In addition, it is also important to establish the exercise habits in children. For these problem solution, the development of "rhythm exercises" with the music is effective.
In this study, I introduce exercise contents to incorporate in "rhythm exercises" to develop. Each exercise component incorporated in "rhythm exercises" is considered by a generative theory of movement.
Moriyama S
Tokyo Gakugei University, Japan
Only two studies investigated relationships between swimming performance and intra-nasal pressure (INP) (Hara et al; 1999 and Moriyama et al; 2014). Two types of breathing rhythm were observed as 1 stroke cycle – 1 breath or 1 stroke cycle – 2 breaths during backstroke swimming (Shibata et al, 2005). Moriyama et al (2014) reported that using comfortable breathing rhythm increases swimming velocity (V) and stroke rate (SR) at competitive swimmers. However, there are no investigations for recreational swimmers. It will be hypothesized that breathing type affects to performance in recreational swimmers as well.
The present study aimed to examine effect on different breathing rhythm on V and stroke indices during backstroke swimming at maximal effort in recreational swimmers.
Nine female collegiate recreational swimmers (height, 1.59 ± 0.04 m; weight, 51.6 ± 4.5 kg) participated in this study. They performed two trials of backstroke swimming for 20 m using the following two different breathing rhythms: Type A, 1 stroke cycle - 1 breath, and Type B, 1 stroke cycle - 2 breaths in their maximal effort. SR and stroke length (SL) were measured as stroke indices. The difference between minimum and maximal values was taken as the INP. V and stroke indices were taken as the mean value of 3 stable stroke cycles and after the center-line were used for analysis. Paired t test was used to test for differences in the swimming velocity, stroke rate and stroke length due to breathing rhythms. The level of statistical significance was set at 5%.
There were no significant differences between Type A and Type B in V, SR, SL and INP (0.55 ± 0.10 m·s-1 vs. 0.56 ± 0.09 m·s-1, 0.34 ± 0.06 Hz vs. 0.35 ± 0.09 Hz, 1.7 ± 0.4 m vs. 1.7 ± 0.5 m and 0.97 ± 0.30 kPa vs. 0.98 ± 0.36 kPa, respectively). Additionally, no significant differences observed in comparisons between breathing rhythm of subjects who felt optimal (confortable) or less optimal (uncomfortable) breathing rhythms at V, SR, SL and INP (0.57 ± 0.09 m·s-1 vs. 0.54 ± 0.10 m·s-1, 0.34 ± 0.06 Hz vs. 0.34 ± 0.09 Hz, 1.7 ± 0.4 m vs.1.7 ± 0.5 m and 0.92 ± 0.28 kPa vs. 1.03 ± 0.37 kPa, respectively).
It is concluded that the breathing type does not affect V and stroke indices for recreational swimmers. Thus, to increase V of recreational swimmers, it may be more effective, for example, to improve backstroke technique and/or physical fitness than finding the suitable breathing type.
Okamura A
Graduate School of Comprehensive Human Sciences, University of Tsukuba, Japan
Recent years has seen the increasing popularity and use of three dimensional motion analysis systems for studies on kinematics and kinetics of body motion. However, certain issues need to be resolved with the use of such a system, namely, the high cost and the delay in feedback to both the players and the coach/staff on the field due to a high-effort analysis time. The purpose of the current study was thus to develop a low-effort and -time body motion analysis system. Here, we present a newly developed system of motion analysis using tennis serve as an example.
The system that our group has developed uses the "Pyhon" as a computer programming language and "OpenCV" as an image processing library. Twenty-serve motions of a University tennis player (male-age; nineteen years old; tennis competition career: six years) were photographed and the control data relating to the success or failure of serves were collected using a home-use digital video camera (Everio, 60 fps; JVC KENWOOD Corp., Yokohama, Kanagawa, Japan) and a tripod. Inputting these data into the system, motion analysis was automatically carried out and analysis results were instantly displayed. The main analysis algorithm used was the principal component analysis (PCA). Motion data was stored as pixel information (=posture information). PCA was carried out based on these data, and the principal components of posture information were extracted followed by calculation of the correlation between each principle score and the success or failure of serves. Synthesizing the principle components which have high correlation to the success or failure of serves, the postures that affect the improvement for performance were visually displayed.
A critical feature of this system is to be able to generate posture improving image data (information) for performance made-to-order. The analysis results were displayed within a few minutes following the input of the obtained data. Posture pattern for a serve which is likely to succeed and posture pattern for a serve which is likely to fail for the subject are visually extracted. The subject was thus able to compare his original motion with the generated computer motion while operating the track bar on the screen. As a result, the subject continued his serve practice with image training using this system for two weeks and improved his performance of serve control.
We believe that this system is useful for players to improve motion with image training because posture information that affects the performance is displayed instantly and visually.
Park ChulHyeong
Jeju National University, South Korea
Students fitness should be a proactive behavior, lack of awareness of fitness physical fitness initiative as missing the real meaning of fitness. In South Korea, football is one of the most popular sports, many students from simple enough to participate in sports activities began to gradually achieve the purpose of fitness through football form. A simple form of football, from the initial fitness no idea gradually aroused the active exercise body awareness.This paper investigats this transition process.
Questionnaires, interviews, comparative method, logical analysis.
Simple form of football can stimulate the enthusiasm of College students. Such as: football games, technical confrontation, a variety of forms of small competitions.It is easy to participate in college students, the whole body into which the heart. And the football itself has a special fitness effect. Survey shows that in the process of sending and receiving and playing on the legs and muscles are to enhance the effect; run on cardiopulmonary function can play an effective exercise; team confrontation can let students enhance physical fitness, mental pleasure.
At first, the form of simple football game, game, cooperation, the impact of the gradual formation of College Students' fitness consciousness. Gradually a strong sense of fitness, the formation of independent sports fitness behavior, eliminate the negative attitude towards life, learning, social, health, and promote the awareness of lifelong physical fitness.
M.D.M.D.Wijesinghe
Department of Education, Faculty of Arts, University of Peradeniya, Sri Lanka
In 21st century the principal's role is very important in developing the quality in education. Like a manager in other business arenas , school principals are leaders of employees. the responsibility of principals are to fulfill the main goals of education created by the ministry of education as well as get goals relevant to their schools and state, social and parents expectations. As an government administrator the principal must have a well balanced personality. For that not only theoretical knowledge soft skills also must be developed to monitor and motivate the performance of teachers and nonacademic staff. As administrators the principals must improve skills of self understanding , self management , social understanding and social skills.
The principals are selected through a competitive examination and they are given a pre service training to develop their personality and give confidence in school management system. But most of their principals with stress and they are not good in physical fitness and disable to control followers. The main aim of the practical training is develop soft skills and hard skills to solve the problems they are faced when playing their roles.
This study aimed to assess the effectiveness of a universal yoga-based social-emotional wellness promotion program, on indicators of newly appointed school principal's emotional distress. Participants included purposively selected12 school principals attending in pre- service training program in Penideniya National College of Education in Sri Lanka.According to my view , I think it can be developed through stress management and yogi exercise.
The action research methodology is adopted in this study. Accordingly , it was implemented using the steps planning , action , observation & reflection. The target group is the new principals who are selected from competitive examinations and recently training to appoint as principals in the future. Data is collected oral questionnaire , written questionnaire and a discussion. Further information are collected through the directors of education , coordinators and the lectures of the training programme . The value of regular Yogi exercise is realized by the principals.
observe whether the principals are improved their physical fitness skills , and participation of the programme through daily yoga exercises. The principals could increased the physical fitness through Yoga exercises.
Results indicated that principals who participated in the basic Yoga program demonstrated significant reductions in anxiety, depression, and global psychological distress. Significant reductions in rumination, intrusive thoughts, physical arousal, and emotional arousal were reported as well. No significant improvements in somatization or general affect were found. Results of this study provide evidence of the potential for newly appointed principals to influence important their social-emotional outcomes among their peers.
The main reason for lack of physical and mental fitness of the principals; is lack of physical training and meditation. A good result could be gained explaining , discussing , paying attention for the target group through the training programme. Through this action research principals could manage their stress and it helps them for correct decision taking and participate in practical activities to develop their skills. It also helps to pay attention of the directors of education to include yogi exercises for pre service training programme for principals.
This action research help to develop professional qualities of the principals and they could face day today problems successfully.